An IP (Internet Protocol) - PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a PBX that provides audio, video and messaging communication through TCP/IP protocol for its internal network and interconnects with the public telephone network for telephony communication. Traditional office PBX systems are being replaced by IP PBX Systems, so that businesses can reduce operating costs by combining traditional PBX functionality with VoIP, and also enjoy the benefits of using a single network for voice and data. The auto attendant feature of our IP PBX systems takes the role of a receptionist and interacts with the customer to route the call. For example, the system asks the customer to "press 1 for sales, 2 for accounts... " etc or "dial the extension number of the person to connect to..." and eventually connects the call to the appropriate personnel.
With a conventional PBX, separate networks are necessary for voice and data communications. One of the main advantages of an IP PBX is the fact that it employs converged data and voice networks. This means that Internet access, as well as VoIP communications and traditional telephone communications, are all possible using a single line to each user. This provides flexibility as an enterprise grows, and can also reduce long-term operation and maintenance costs. Like a traditional PBX, an IP PBX is owned by the enterprise.
How an IP PBX / VoIP Phone System Works
A VoIP Phone System / IP PBX system consists of one or more SIP phones / VoIP phones, an IP PBX server and optionally includes a VoIP Gateway. The IP PBX server is similar to a proxy server: SIP clients, being either soft phones or hardware based phones, register with the IP PBX server, and when they wish to make a call they ask the IP PBX to establish the connection. The IP PBX has a directory of all phones/users and their corresponding SIP address and thus is able to connect an internal call or route an external call via either a VoIP gateway or a VoIP service provider to the desired destination.
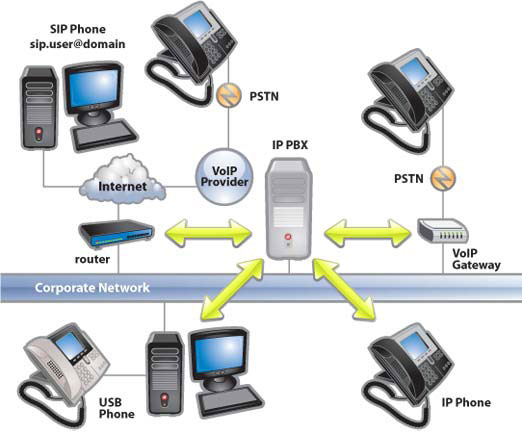
At the center we have, the IP PBX. Starting from the bottom, we see the Corporate Network. This is the company's local network. Through that network, Computers running SIP clients such as the 3CX softphones, and IP Phones connect directly to the PBX. On the left, we see the company's router/firewall connected to the internet. From there it can connect to remote extensions in the form of computers running the softphones, remote IP Phones, mobile devices running the 3CX Android and iOS clients, and Bridged PBX's. Using a VoIP provider we can connect to the PSTN network. To the right a VoIP Gateway connects the PBX directly to the PSTN network.
© 2016 Salient IT Systems. All rights reserved.
